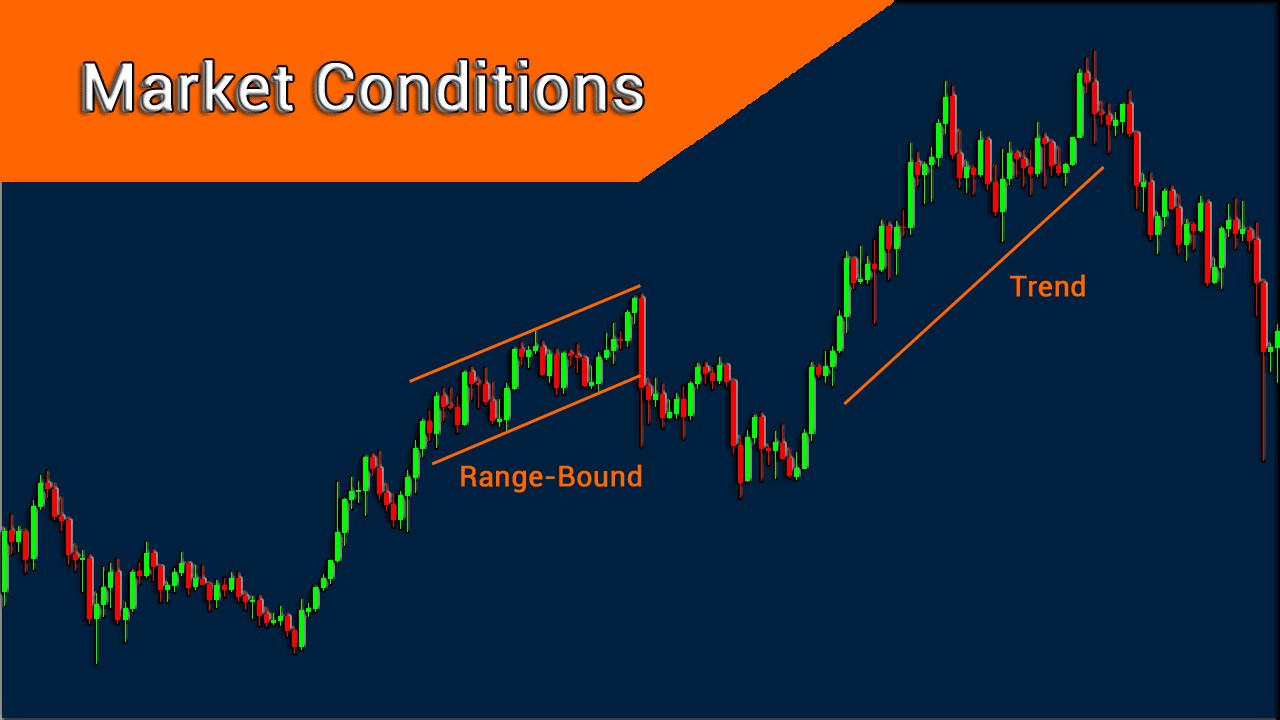
Market conditions is a term that refers to the state of an industry or economy. The term is often used to describe the stock markets and real estate markets, which are often described as volatile or stable. These situations are symbols that many people use to influence their decisions. However, these indicators do not translate in the same way for all parties. Moreover, they generally cannot be relied upon for long periods of time without reassessment because market conditions are rarely permanent.
The volatility of markets is driven by many different factors. A prime example is finance. Money flow, credit availability, and firm employment play important roles in shaping markets locally, nationally, and globally. Thus market conditions can refer to the general conditions or the conditions of a particular industry.

Consider the stock market , which is very broad because it is made up of interested people in many different industries. During periods when an economy is generally viewed as negative, the fund can suffer because investors may put in less money than they had before. In this case, overall, the market can be summarized as downward.
However, the fact that the market is down may not be representative of the state of any business or business in the stock market. There may be specific industries, such as precious metals, that perform exceptionally well during this period. However, in the precious metals industry, there may be some companies that are not performing very well.

People often take note of market conditions to help them make certain decisions. This can be particularly important for businesses and investors. However, it is important for decision makers to avoid over-reliance on general definitions. At the same time, it may also be important for individuals to avoid ignoring market conditions or factors that are influencing them.
Market conditions are important indicators. They often specify who should act and in what position at a particular time. For example, depending on the nature of the real estate industry, it can be considered a buyer’s market or a seller’s market. This means that conditions at a given time favor one group over another. In a buyer’s market, sellers may prefer to hold their assets because they are worth less, and if they decide to take action, they will incur losses.
Although the situation can be described as volatile or stable over a period of time, actual market conditions are generally volatile. Circumstances can change quickly or over time. For this reason, companies and investors cannot rely solely on current conditions for a long time without further reassessment. Doing so would lead to decisions based on outdated indicators, which could be devastating.
What Are the Four Conditions of Market Disclosure?
A purely competitive market, also known as a perfectly competitive market, includes a theoretical market structure characterized by four specific situations: a large number of buyers and subsidiaries, sellers with identical products,; no restrictions on entry and exit from the market, and full knowledge of products and prices available to buyers and sellers. This model exists only when these conditions exist.
More Buyers, More Sellers
Unlike in a monopoly system, there is no single firm in a purely competitive market.
There are also more buyers, and with that the number of sellers stabilizes supply and demand.
Equivalent Materials
Consumer preferences play little role in a purely competitive market because products have no distinctive features. As a result, prices are determined by supply and demand, not sellers. This is known as a price cap, in which firms must accept market prices or risk losing business. Raising prices by even a fraction will drive consumers to competitors.
Free Entry and Exit
In a purely competitive market, businesses have no barriers to entry and exit from the market. Weak or no government regulation and low start-up costs make it easier for new companies to enter the market.
Relevant Information for Sellers and Buyers
The measurement system in a purely competitive market provides buyers and sellers with complete and accurate information about prices and products being sold. Detailed product information may include manufacturing processes, product specifications, and quality indications. This knowledge supports the decision-making process for consumers and entrepreneurs.
One criticism of this market system is that it is a pendulum that rarely swings. Production, price, quantity supply and demand generally remain stagnant, with little or no room or incentive for innovation.
What Conditions Must Be in Place for a Store Exchange to Happen?
A trade exchange is when two or more parties are involved in the transfer of goods, services, or intellectual property. This is a lucrative arrangement in which each participant gains something of value by providing a lucrative commodity that the other party wants in return. Five conditions must be met for flexibility:
- There should be at least two parties. Exchange potential exists only when at least two parties are interested in facilitating a transaction.
- Each side must have something that the other values. For successful change to occur, everyone involved must be confident that they are getting more than they are giving.
- Everyone involved in the change needs to be willing and able to communicate effectively, manage agreed expectations and track deliverables. Establishing and maintaining trust is key to ensuring satisfactory performance and future changes.
- All parties must be able to accept or reject the terms proposed in an amendment. The intended outcome of any marketing revolution is to find something that satisfies a particular want or need. Each party should be free to negotiate if supplies are considered inadequate or unsatisfactory. They should also choose to withdraw as long as there is no breach of any legal contract.
- Each party is committed to the exchange and can trust that the other party will approach the transaction with the same objectives. Before starting the exchange, interested parties should determine the suitability of the candidates. Once both parties are on board, all documentation regarding the transition should be clear, respectful, and sincere.
What Conditions Can Make a Market Work?
An ideal market balances supply and demand. Any disturbance of the equilibrium can lead to market failure , namely the inefficiency of planning, production, distribution, and distribution of goods and services. Market failures can occur for a number of reasons but are usually attributed to one or more of the following factors: negative externalities, societal factors, and inadequate market control.
Harmless Exteriors
Externalities refer to results brought to bear on a party not directly involved in marketing activities. These effects can generate benefits (positive externality) or impose undesirable costs (negative externalities). Excessive noise, pollution, and congestion are examples of negative externalities that can adversely affect markets by creating moral, political, social, or public health issues.
Public Goods
Public goods such as national defense, education, and infrastructure are provided by a central agency, usually the government, to all consumers regardless of ability to pay. As a result, it is nearly impossible to produce an optimal number of public goods.
Undue Market Pressure
In a monopolistic system, one seller holds most of the market power. This control focus effectively eliminates competition that leads to shortages, poor quality, and high prices.